

Some bar graphs present bars clustered in groups of more than one (grouped bar graphs), and others show the bars divided into subparts to show cumulative effect (stacked bar graphs). One axis of the chart shows the specific categories being compared, and the other axis represents a discrete value.
A bar graph is a chart that uses either horizontal or vertical bars to show comparisons among categories. That is, finding a general pattern in data sets including temperature, sales, employment, company profit or cost over a period of time. These graphs are useful for finding trends.

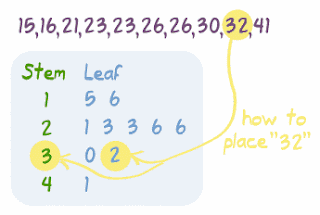
A line graph is often used to represent a set of data values in which a quantity varies with time. The advantage in a stem-and-leaf plot is that all values are listed, unlike a histogram, which gives classes of data values. In a stem-and-leaf plot, all data values within a class are visible. The frequency points are connected using line segments.Ī stem-and-leaf plot is a way to plot data and look at the distribution. In the particular line graph shown in Example, the x-axis (horizontal axis) consists of data values and the y-axis (vertical axis) consists of frequency points. Do not put a depth on a line that contains no leaves.\) Atlanta Hawks Wins and Losses Number of WinsĪnother type of graph that is useful for specific data values is a line graph. If the median fall between two lines, the depths of those two lines will be the same (and each will be half of the total sample size). For the stem line that contains the median, count the number of leaves on the stem and put that number in parentheses. These indicate the depths of the values on that line to the closest end of the data set. Counting from each end, indicate to the left of each stem the total number of leaves from that line to the nearer end of the data set. If the 62.3 were split as 62 3, the example would be, Unit =. At the top of the display, indicate the unit of the leaf with a decimal point, and by providing an example such as in the case of 623 split as 6 2, Unit = 10 12 = 120 Extreme outliers can be simply listed as LO and HI on each end of the distribution. Five lines per stem: Place leaves 0 and 1 on a line labeled ∙, leaves 2 and 3 on a line labeled T (Two and Three), leaves 4 and 5 on a line labeled F (Four and Five), leaves 6 and 7 on a line labeled S (Six and Seven), and leaves 8 and 9 on a line labeled *.Ħ. Two lines per stem: Place leaves 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 on the first line (indicated by a ∙ after the stem), and leaves 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 on the second line (indicated by a * alone).ī. The choice of how many lines to use per stem is also dictated by how the final display looks.Ī. The two most commonly used arrangements are two lines per stem and five lines per stem. When there are a large number of values, two or more lines can be used per stem. The leaves should be arranged in ascending order on each stem. Locate the stem for each number and write the leaf (first trailing digit) on that stem line. Mode is a measurement not often affected by outliers. Doing this shows that it is not actually an outlier. Sometimes we may have to compare different stem/leaf splits to find the one that creates the most informative display.Ĭreate a column of all of the possible stems from lowest to highest in the present data set.ĭraw a vertical line to separate the stems from the leaves. While 19 is a possible outlier (since there is a gap in the stem plot), it is worth checking this with the 1.5 IQR criterion.

The choice of where to place this split is governed by how the final display looks. In the second case, 6 is the stem and 2 is the leaf. In that case, 62 is the stem and 3 is the leaf. For example, the number 623 can be split into 62 3 or 6 2 (throwing away the 3). To provide a representation of all of our data which is both a graph and a table.Ĭhoose a pair of adjacent digit positions to split all numbers in the data set into stems and leafs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
